Difference between revisions of "S-787"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
SHELTER, STANDARDIZED INTEGRATED COMMAND POST (SICPS) MODEL S-787/G, TYPE II | SHELTER, STANDARDIZED INTEGRATED COMMAND POST (SICPS) MODEL S-787/G, TYPE II | ||
[[File:S-787.G TYPE II. 01.jpg]] | [[File:S-787.G TYPE II. 01.jpg]] | ||
| + | [[File:S-787.G TYPE II. 02.jpg|800px]] | ||
Citation of Wenzlau: | Citation of Wenzlau: | ||
Revision as of 12:43, 31 December 2017
SHELTER, STANDARDIZED INTEGRATED COMMAND POST (SICPS) MODEL S-787/G, TYPE II
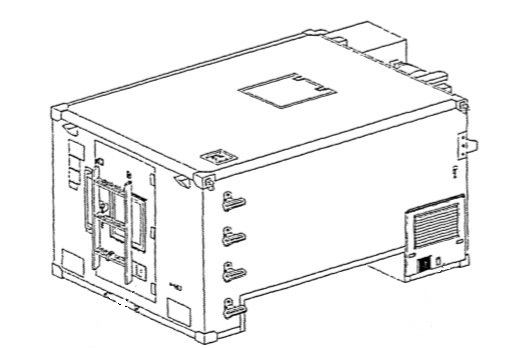
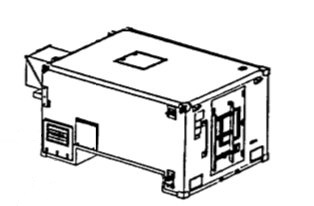
Citation of Wenzlau: Ever since the Army had need for centralized communications in the field, the command post was a shack, tent, bunker, foxhole or wherever soldiers could locate a safe place to set up an antenna and a radio. All this has changed with the development of a Standardized Command Post by SSCOM’s Natick Research, Development and Engineering Center (NRDEC). The Standardized Integrated Command Post System (SICPS) Rigid Wall Shelter (RWS), S-787, is a lightweight, transportable, protected shelter mountable on the heavy HMMWV.
The SICPS RWS is equipped with the following components: 10 kW lightweight APU, 18,000 BTU/hr ECU (manufactured by EEI), 100 cubic feet per minute CB filter, equipment racks and operator seat. Incorporated into the shelter are power/signal panels and wiring appropriate for the Army Tactical Command, Control and Communications System (ATC3S). These features include antenna mounts, telephone connections, and coaxial and fiber optic Local Area Network connections. A cargo trailer, which carries the Modular Command Post System Tent (MCPS) and camouflage, is towed behind the HMMWV. To gain access to and from the tent, the MCPS interfaces with the RWS by forming a boot-wall passageway and is set up when a CP remains in the same location for more than a few hours. A MCPS measures 11’ x 11’, is frame supported, and has interchangeable sidewalls that can be configured in any design to meet the needs of the field commander. This feature allows several mobile units to park in a cluster to form a battalion sized CP.
To save weight, the APU is mounted in its own compartment within the RWS and uses the HMMWV battery for starting and HMMWV fuel for operating. The APU is a modified commercial item featuring a turbocharged diesel engine that operates at 3600 RPM and produces 220 volt, single-phase, 3-wire power to operate the ECU. The APU is approximately 150 pounds lighter than the 5 kW unit it replaced. The electrical cable raceway layout design inside the RWS separates power and signal cables. This minimizes and standardizes cable lengths for easy replacement. All blackout and utility lights run off the battery.
The interior of the RWS contains a standardized layout of equipment racks attached from floor to ceiling, capable of holding 925 pounds of mission equipment, twice the weight of the previous RWS version. The cables run along the side and front walls behind the equipment racks. The equipment operator's seat was modified for comfort.
Part of the ECU, the condenser, has been mounted directly on the outside, front wall, of the RWS over the HMMWV cab. The evaporator, which delivers the cool air, is located on the inside. This design doubles the cooling capacity of the previous ECU.
Reference Files
- TM 10-5411-222-24P
- TB 10-5411-222-24
See Also
S-788 The other SICPS of General Dynamics