Difference between revisions of "AN~MPQ-2"
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
[[File:AN.MPQ-2A.jpg]] | [[File:AN.MPQ-2A.jpg]] | ||
| + | =Components= | ||
| + | 1. Antenna Control [[C-484]]/MPQ-2A (1) | ||
| + | |||
| + | 2. Antenna [[AT-160]]/MPQ-2A (1) | ||
| + | |||
| + | 3. Azimuth & Elevation Indicator [[ID- 248]]/MPQ - 2A (1) | ||
| + | |||
| + | 4. Coder [[KY-31]]/MPQ-2A (1) | ||
| + | |||
| + | 5. Control Panel [[C-482]]/MPQ-2A | ||
| + | |||
| + | 6. Control Unit [[BC-1085]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | 7. Data Unit [[BC-1075]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | 8. Dehydrator | ||
| + | |||
| + | 9. Distribution Panelboard [[J-278]]/MPQ-2A | ||
| + | |||
| + | 10.Driver Unit [[BC-1080]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | 11.Indicator [[BC-1092]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | 12.Junction Box [[JB-71]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | 13.Modulator [[BC-984]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Oscillator BC-1096 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Pedestal MP-61 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Power Supply PP-325/MPQ-2A | ||
| + | |||
| + | Power Supply Unit RA-132A | ||
| + | |||
| + | Pre-Amplifier AM-220/MPQ-2A | ||
| + | |||
| + | Radio Receiver BC-1056-D | ||
| + | |||
| + | Range Indicator ID-237/MPQ-2A | ||
| + | |||
| + | Range Tracker C-483/MPQ-2 | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 15:20, 29 August 2018
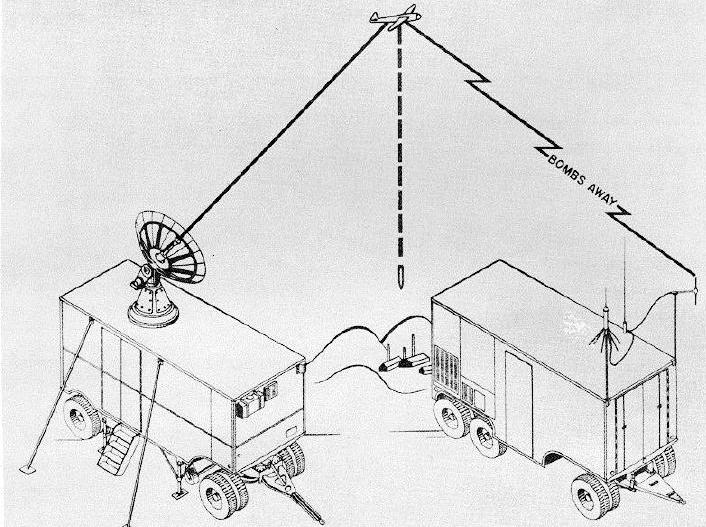
The AN/MPQ-2 Close Cooperation Control Unit was a truck-mounted post-World War II automatic tracking radar/computer/communication system ("Q" system) for aircraft command guidance, e.g., missile tracking, and for Radar Bomb Scoring. For ground directed bombing (GDB), an operator would manually plot a target on the "Blind Bombing Plotting Sheet", then use the manual "E6B computer and bombing tables" to plot the release point for striking the target, after which a radar operator used the MPQ to acquire a track of the bomber near an initial point during which allowed ground control of the bomb run to the release point.
Based on the World War II SCR-584 radar developed by MIT and which was used for the "SCR-584-M missile control Receiver and beacon", the MPQ-2 included an "Reeves Instrument Corporation RC-294 Plotter" and its analog computer for converting radar range, azimuth, and elevation to cartesian coordinates, as well as a plotting board for drawing the aircraft track. The AN/MPQ-2 was the basis for the Rome Air Development Center's AN~MSQ-1 & -2 Close Support Control Sets also used in the Korea and the MSQ-1A was used for command guidance of the Matador missile.
Contents
Locations
Radar Bomb Scoring detachments of the Colorado Springs Tent Camp|Colorado Springs' 206th Army Air Force Base Unit]] (organized on June 6, 1945) used MPQ-2s at Kansas City, and Fort Worth Army Airfield, and in 1946, the List of V-2 test launches Launches of captured V-2 rockets in the USA after 1945 4th launch of a V-2 at White Sands Proving Ground (1946) was tracked by two MPQ-2s. In addition to the CONUS RBS detachments (e.g., Detachments C, K, & N), Detachment 23's AN/MPQ-2 was at the South Ruislip Heston Radar Bomb Scoring Site on November 10, 1950, and after deployment to the Korean War, the three AN/MPQ-2 radars of the 3903rd Radar Bomb Scoring Group RBS detachments were transferred in January 1951 under the operational control of the 502nd Tactical Control Group (TCG). The MPQ-2 guided Martin B-26 Marauders against enemy positions in front of the 25th Infantry Division.", and On February 23, 1951, the 1st Boeing B-29 Superfortress mission controlled by an MPQ-2 was flown,
AN/MPQ-2A
Components
1. Antenna Control C-484/MPQ-2A (1)
2. Antenna AT-160/MPQ-2A (1)
3. Azimuth & Elevation Indicator ID- 248/MPQ - 2A (1)
4. Coder KY-31/MPQ-2A (1)
5. Control Panel C-482/MPQ-2A
6. Control Unit BC-1085
7. Data Unit BC-1075
8. Dehydrator
9. Distribution Panelboard J-278/MPQ-2A
10.Driver Unit BC-1080
11.Indicator BC-1092
12.Junction Box JB-71
13.Modulator BC-984
Oscillator BC-1096
Pedestal MP-61
Power Supply PP-325/MPQ-2A
Power Supply Unit RA-132A
Pre-Amplifier AM-220/MPQ-2A
Radio Receiver BC-1056-D
Range Indicator ID-237/MPQ-2A
Range Tracker C-483/MPQ-2